How to protect skin from sun
By Catalogs Editorial Staff
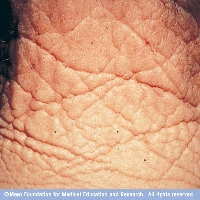
Learn how to protect skin from sun and start early to stay looking great!
Your skin has to last you a lifetime. How well it looks and its health at the end of the road depends on how diligently you have taken care of it or neglected it.
First and foremost, you must protect your skin from the sun. The UV rays from the sun are terribly damaging to skin.
Fifty years ago, sunbathing became a popular pastime for many women and men. The darker the better, was the motto. Sunscreen was non-existent at the time although there was Coppertone suntan lotion and oil, which afforded some protection.
Down the road, the sun worshipers paid the price and suffered from terribly and prematurely wrinkled skin and, often, skin cancer.
Approximately 80 percent of an individual?s lifetime sun exposure occurs before the person is 18 years old. Parents need to make sure that their children are aware of the dangers of the sun and insist that they use an effective sunscreen product.
When a person is exposed to too much sun, the UV or ultraviolet light harms the fibers or elastin in the skin, causing the fibers to break down. When this happens, skin stretches, sags and isn?t capable of rebounding after it is stretched. Skin starts to tear and bruise more easily and healing time is longer than it once was.
SKIN LAYERS
The top layer of skin is the epidermis. It consists primarily of kerantinocytes, which are cells that start in the deepest layer of the epidermis and are then pushed upward toward the surface of the skin when more cells are produced underneath them. By the time keratinocytes reach the surface they?re dead. These dead cells provide waterproofing and protection to the layers underneath.
The base for the epidermis is the dermis. It is full of collagen, which is what gives skin resistance to damage and resilience as well as strength. When there is ample collagen, skin can be stretched but recoils to its original shape easily. There are also sweat glands and hair follicles in this layer of the skin.
Between the epidermis and the dermis are melanocytes, which are cells that produce melanin or dark pigmentation when the skin has been exposed to sun. The melanin is absorbed and used by the keratinoctyes to provide protection from UV rays.
Melanin is a built-in sunscreen because it absorbs incoming UV rays, which is what makes a person become tanned. Those people who naturally tan easily have more protection and have less risk of acquiring skin cancer. Fair skinned don?t have as much melanin.
THE RESULTS OR PAYING THE PIPER
Sun damaged skin is often freckled, wrinkled, yellow or a sallow color, and the pigmentation of the skin becomes mottled (discolored.) Benign tumors can crop up as well as actinic kurtosis, which is a precancerous skin lesion. Other possibilities are basal cell carcinoma, melanoma and squamous cells carcinoma, which are cancerous lesions. These are the result of impaired skin immune function due to over exposure to the sun.
Sun damaged skin is likely to expose the small blood vessels under the skin because the vessels have become dilated, which is called telangiectasia.
Elastosis occurs, which is the destruction of the elastic tissue in the skin, which leads to wrinkles and lines.
~
The worst kind of skin cancer is melanoma, which is responsible for three-quarters of all skin cancer fatalities. If it is not treated, it can travel to other body organs. Melanoma is the result of bad sunburns that have occurred before the age of 18, while squamous and basal cell cancers are the result of cumulative sun exposure. Squamous cells and basal cells cancers are not as treacherous as melanoma but still should be taken seriously and treated early.
If you are blonde or have red hair and fair skin that burns easily you are more at risk than your dark skinned counterpart, although he, too, must be careful. If you have a family history of skin cancer, this increases your risk, as well as living where it?s hot and sunny all the time or working outdoors.
Severe sunburns that occurred in the past can cause irregularly shaped moles that are large and pop up all over. These moles are indicators that you are at risk for melanoma.
HELP! HOW TO PROTECT YOUR SKIN
How do you protect your skin from cancer? Sunscreen, with a SPF or sun protection factor of 15 or greater, should always be applied before going out into the sun. Reapply it every few hours if you remain out in the sun.
Do not go outside during the peak UV radiation hours which occur between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. Protect your eyes by wearing sunglasses with UV protection and use UV protective products on your skin, in your hair and wear contact lenses that contain of UV protection.
Give your body a good going over once a month. Look very carefully to see if any new moles have emerged. If they have, you may want to consult with your physician or dermatologist. Have any of the moles changed in size, shape or color? This is something else that you need to be on the look-out for.
No one is suggesting that you should avoid the sun altogether; just be smart about it. Talk to your children while they are young and explain to them that swimming, boating and playing ball in the sunshine are wonderful activities but they need to wear sunscreen. This protects their skin and helps prevent avoid sunburns, which are horribly painful and have lasting consequences.
Popular Savings Offers











